Bitcoin Highlights the Virtues of Quantitative Hardening
Bitcoin Quantitative Hardening is to be contrasted with the Quantitative Easing led by the Fed.

Since the beginning of the coronavirus crisis, you have probably heard several times about quantitative easing. If you find the economy, and particularly the monetary and financial system, too complex, you may not have reacted immediately when you heard this term come back into the limelight.
However, the unlimited quantitative easing program conducted by the Fed since March 23, 2020, will have a strong impact on your daily life in the weeks and months to come. The inflation of the money supply in the U.S. dollar that this will necessarily induce is likely to lead to a strong currency devaluation.
The U.S. dollar being the world’s reserve currency, the United States will once again export its inflation. Other central banks have already started to conduct quantitative easing programs.
If we are far from the $8T of liquidity printed by the Fed, the European Central Bank is already above $1.3T printed, and the Bank of China is close to $500 billion.
You must therefore absolutely try to understand what quantitative easing is in order to prepare yourself as well as possible for the consequences that it will have on your daily life in the weeks and months to come.
Quantitative Easing Is the Fed’s Systematic Approach
First of all, I’m going to start with a little bit of theory. Quantitative easing, often abbreviated to QE in the literature, is a monetary policy that can be followed by a central bank.
Quantitative easing involves buying a predetermined amount of government bonds or other financial assets in order to add money directly into the economy.
This unconventional monetary policy requires the central bank in question to first set the stage by lowering interest rates. As you may recall, this is what the Fed did in March 2020 by lowering interest rates by a total of 150 basis points.
With interest rates at zero, the Fed was in an ideal position to conduct a policy of quantitative easing, which is like printing the U.S dollar.
In fact, it had no choice once interest rates had been lowered to the previously taboo level of zero. Indeed, if the Fed had not acted, it would have intensified the liquidity crisis we experienced in mid-March 2020.
This liquidity crisis was exacerbated by the fact that we were at the end of a bull market cycle in financial markets such as Wall Street.
At the end of such a cycle, the majority of people have no more cash on hand because they have invested everything without keeping a minimum of cash on hand.
With its unlimited quantitative easing program, the Fed will probably happen to exceed $10T of liquidity injection in the coming weeks.
This quantitative easing monetary policy had already been the solution adopted by the Fed and other central banks at the end of the previous crisis. Nevertheless, at the time, the bill was more like hundreds of billions of dollars.
Quantitative Easing Produces Fewer and Fewer Tangible Effects
Unfortunately, quantitative easing is a monetary policy that comes with its own set of drawbacks. The first disadvantage of quantitative easing is that the induced increase in the money supply will lead to currency devaluation.
Thus, people who own the majority of their wealth in cash will be penalized compared to those who own real estate, gold, or shares on the financial markets.
For an individual, fighting against the effects of quantitative easing, therefore, consists of spending his cash to buy illiquid assets, shares, or gold. Unfortunately, a lot of people are unable to do this.
Again, these are mainly the poorest people.
People who are already rich and who have this kind of asset will be enriched by a quantitative easing policy. It will not surprise you to know that the powerful people at the head of the monetary and financial system are in a situation where they have a lot of assets that will increase in value under these conditions.
A quantitative easing policy will therefore hit even harder those who would need even more support in times of economic crisis such as the one we are about to experience.
The second problem with quantitative easing is that it only postpones the problems to later. During the economic crisis of 2008, the world’s major economic powers preferred to resort to this easy money policy rather than attacking the root of the evil.
The result is disastrous because the problem will return in the future in an even more violent manner.
The economic crisis we are experiencing today is therefore only the unfortunate and logical continuation of the 2008 crisis, which was not really resolved, but merely postponed.
What complicates things is that with each postponement of the problem, the amounts to be injected within the framework of quantitative easing will increase greatly.
If hundreds of billions of dollars had been enough in 2008 to plug the leaks on the ship, we are talking trillions of dollars today.
With the quantitative easing programs being followed by the major central banks today, it is quite conceivable that in the next economic crisis 10 years from now we would be talking in quadrillions of dollars.
So you have understood that these quantitative easing policies are just a never-ending story, which only pushes back the problem without really solving it. With one constant: with each postponement of the problem, it becomes even bigger the next time.
Quantitative Hardening Is the Other Possible Route
Now that you have become aware of the problems associated with quantitative easing, you must ask yourself if there is an alternative. Contrary to what powerful people in the monetary and financial system try to make us believe, an alternative to quantitative easing does exist.
The alternative to quantitative easing (QE) is quantitative hardening (QH).
Quantitative hardening consists in reducing the liquidity injected into a market over time by reducing the daily supply available. In this way, each unit of that market gains in value over time.
This policy is clearly the opposite of quantitative easing where the daily supply keeps increasing, which further weakens the value of the units available on the associated market.
As an example, the U.S. dollar money supply, represented by the M2 Money Stock Index, increased by 6.7% in March 2020 alone as a result of the Fed’s liquidity injections:
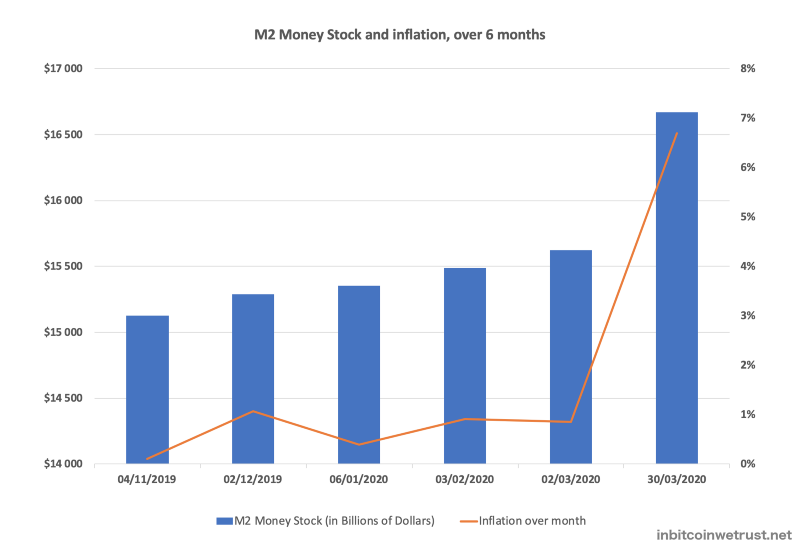
If you imagine that you had $10,000 in cash at the beginning of March 2020, what you own has gone from $10K on $15.5T to $10K on $16.6T.
You immediately understand that the purchasing power associated with your $10K will necessarily be reduced thereafter.
Bitcoin Has a Quantitative Hardening Monetary Policy
Now, the big question you have to ask yourself is what solutions exist with a quantitative hardening type policy. You must have heard about this solution for several years now: it is called Bitcoin.
Created by Satoshi Nakamoto following the 2008 crisis, Bitcoin should be seen as a response to the excesses of the monetary and financial system.
Bitcoin has a unique monetary policy:
- A maximum supply is known in advance and set at 21 million.
- A maximum offer that will never change.
- The inflation of new Bitcoins produced on a daily basis will continue to decrease over time.
In addition to these unique properties, Bitcoin’s monetary policy is automatic. It is written in Bitcoin’s source code and therefore does not depend on any human decision, which by definition would be arbitrary.
With Bitcoin’s monetary policy, everything is predictable.
The Bitcoin reward that is paid to miners who validate a block of transactions is what allows the creation of new Bitcoins. In order to decrease the inflation of the Bitcoin supply over time, this reward is divided by two for every 210,000 blocks of transactions added to the Blockchain.
This decrease of the reward is called Halving.
In order to ensure that this happens approximately every 4 years, the difficulty for mining new blocks on the Bitcoin Blockchain is adjusted every 2016 block, so that one block is added approximately every 10 minutes.
Originally, the Bitcoin reward for miners was 50 BTC. After the first division of the reward amount in 2012, it was decreased to 25 BTC. After the second Halving in 2016, the reward decreased to 12.5 BTC.
In May 2020, during the third Halving of Bitcoin, the reward will decrease to 6.25 BTC.
Thus, with an average of 144 mined blocks per day, the production of new Bitcoins will now be around 900 per day, compared to 1800 since 2016.
This Bitcoin monetary policy will lead us to annual inflation of the Bitcoin supply below 2% as soon as 2021. It will then be 1.8%:
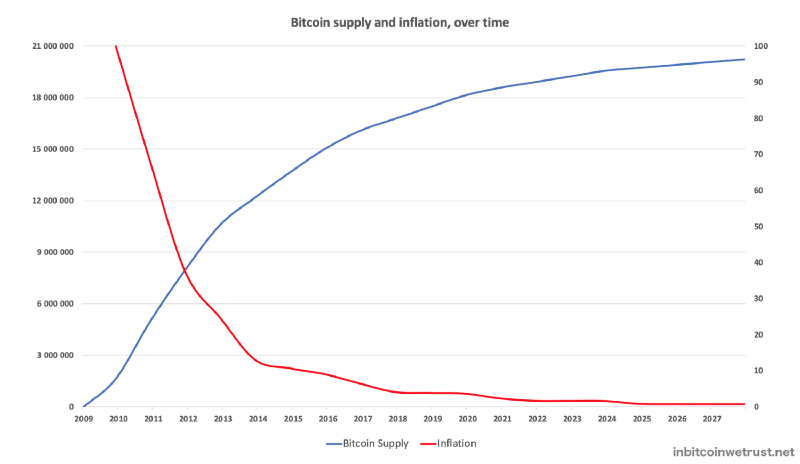
Bitcoin’s quantitative hardening policy will bring the annual inflation of the Bitcoin supply below 1% as of 2024 at the fourth Bitcoin Halving.
This inflation will continue to trend towards zero, reaching zero around 2140 when the 21 million Bitcoins will have been mined.
Bitcoin Highlights the Virtues of Quantitative Hardening
Quantitative hardening is a concept that will intrigue more and more people in the months and years to come. This monetary policy, which is Bitcoin’s policy, corresponds to a total paradigm shift from the current fiat system.
Bitcoin encourages you to save what you own because it values your Bitcoins over time.
Since the inflation of the Bitcoin supply is constantly decreasing over time, each unit of Bitcoin becomes more valuable as demand increases. The principles of the law of supply and demand explain this clearly.
It is therefore in your interest to keep your Bitcoins for the long term. By becoming a Bitcoin HODLER, your support for the Bitcoin revolution will be rewarded with the appreciation of the price of each unit of Bitcoin.
As you read this article, I hope that you have understood that there is another way out of the current monetary and financial system. This alternative path emerged as a result of the economic crisis of 2008, and it is our best solution in the face of the crisis that is now beginning.
Bitcoin, which represents this other path, will still be there during the next economic crisis in 10 or 15 years, but I have a feeling that its price will no longer be $7K as it is today.
To tell the truth, I think Bitcoin price will already be over 6 figures when the next economic crisis will occur in 10 years.
Why? Simply because of its quantitative hardening policy which will give day after day, block after block, Halving after Halving, more and more value to the units of Bitcoin in circulation.
Nevertheless, during the next economic crisis in 10 years, when central banks’ liquidity injections will be counted in quadrillions, you may unfortunately no longer have such an interesting opportunity to opt-out of the current system by buying Bitcoin.
As always, the decision is yours. The most important thing is that you educate yourself properly in order to make the best decisions for your future so that you will have no regrets in 5 or 10 years’ time.







7 Responses
[…] Bitcoin Halving will cause a real shock on the Bitcoin supply which will highlight the virtues of quantitative hardening. In contrast to the quantitative easing practiced by the Fed and other central banks, quantitative […]
[…] can choose to exchange your fiat currency for Bitcoin. Bitcoin has a quantitative hardening monetary policy that protects what you own. Better yet, Bitcoin increases in value over time. Your wealth increases simply by […]
[…] Bitcoin Highlights the Virtues of Quantitative Hardening […]
[…] Bitcoin highlights the virtues of quantitative hardening. […]
[…] Bitcoin Highlights the Virtues of Quantitative Hardening […]
[…] Bitcoin highlights the virtues of quantitative hardening. […]
[…] While central bankers constantly point out the limits of quantitative easing, Bitcoin points out the many benefits to the people of quantitative hardening. […]